For older people and frail people, the long-term benefit of medicines reduces and the potential for harm from adverse effects increases. When the benefit–risk balance changes in this way, medicine review and optimisation are important to simplify the therapeutic regimen, reduce inappropriate medicines and minimise risks. In this article, pharmacist prescriber Linda Bryant uses two case studies to illustrate important considerations during medicine reviews
Appreciating gastrointestinal side effects of prescribed medications
Appreciating gastrointestinal side effects of prescribed medications
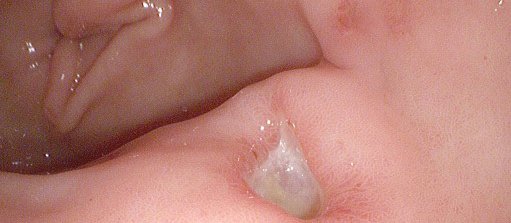
Prescribers need to be continually mindful of the potential harms from medication. Here, gastroenterologist Alan Fraser outlines the various gastrointestinal side effects of prescribed medications
Kia ora and welcome to New Zealand Doctor Rata Aotearoa
Not a subscriber? Unlock this article by subscribing here.
1. Tomlin A, Woods DJ, Lambie A, et al. Ethnic inequality in non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drug‐associated harm in New Zealand: A national population‐based cohort study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2020;29:881–89.
2. Jahromi SR, Togha M, Fesharaki SH, et al. Gastrointestinal adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs in intractable epileptic patients. Seizure 2011;20(4):343–46.




![New Zealand Doctor Rata Aotearoa editor Barbara Fountain, RNZCGP president elect and Tauranga-based specialist GP Luke Bradford, Ministry of Health clinical chief advisor rural health Helen MacGregor, and Health New Zealand Te Whatu Ora clinical director primary and community care Sarah Clarke [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/1.%20Barbara%20Fountain%2C%20Luke%20Bradford%2C%20Helen%20MacGregor%20and%20Sarah%20Clarke.jpg?itok=091NETXI)
![Ngāti Porou Oranga specialist GP Elina Pekansaari and Te Nikau Hospital specialist in general practice and rural hospital medicine David Short [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/2.%20Elina%20Pekansaari%20and%20David%20Short.jpg?itok=h5XfSBVM)
![Locum specialist GP Margriet Dijkstra and OmniHealth regional operations manager (southern) Patricia Morais-Ross [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/3.%20Margriet%20Dijkstra%20and%20Patricia%20Morais-Ross.jpg?itok=jkrtRfJC)
![Golden Bay dairy farmer and dairy industry health and safety doctoral student Deborah Rhodes, and Golden Bay Community Health specialist GP Rachael Cowie [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/4.%20Deborah%20Rhodes%20and%20Rachael%20Cowie.jpg?itok=oM0_GcJc)
![Hauora Taiwhenua clinical director rural health Jeremy Webber, Australian College of Rural and Remote Medicine president Rod Martin and Observa Care director of business operations Deborah Martin, the wife of Dr Martin [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/5.%20Jeremy%20Webber%2C%20Rod%20Martin%20and%20Deborah%20Martin%2C%20the%20wife%20of%20Dr%20Martin.jpg?itok=P_aGmX_H)
![Spark Health chief executive John Macaskill-Smith and client director Bryan Bunz [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/6.%20John%20Macaskill-Smith%20and%20Bryan%20Bunz.jpg?itok=5yJvVZ0I)
![Associate dean (rural) Kyle Eggleton, third-year medical student Roselle Winter, and second-year pharmacy student Alina Khanal, all from the University of Auckland [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/7.%20Kyle%20Eggleton%2C%20Roselle%20Winter%20and%20Alina%20Khanal.jpg?itok=RQLd3TEs)
![Health New Zealand Te Whatu Ora clinical editor and specialist in general practice and rural hospital medicine Anu Shinnamon, and Whakarongorau chief clinical officer Ruth Large [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/8.%20Anu%20Shinnamon%20and%20Ruth%20Large.jpg?itok=i5TMswY9)
![Te Kahu Hauora Practice specialist GP Jane Laver and Ngāti Kahungunu ki Tāmaki-nui-a-Rua chief operations manager Tania Chamberlain [Image: NZD]](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_cropped_100/public/2025-05/9.%20Jane%20Laver%20and%20Tania%20Chamberlain.jpg?itok=jtMklaCZ)