For older people and frail people, the long-term benefit of medicines reduces and the potential for harm from adverse effects increases. When the benefit–risk balance changes in this way, medicine review and optimisation are important to simplify the therapeutic regimen, reduce inappropriate medicines and minimise risks. In this article, pharmacist prescriber Linda Bryant uses two case studies to illustrate important considerations during medicine reviews
Flu in a post-COVID world: Learnings from SHIVERS-V
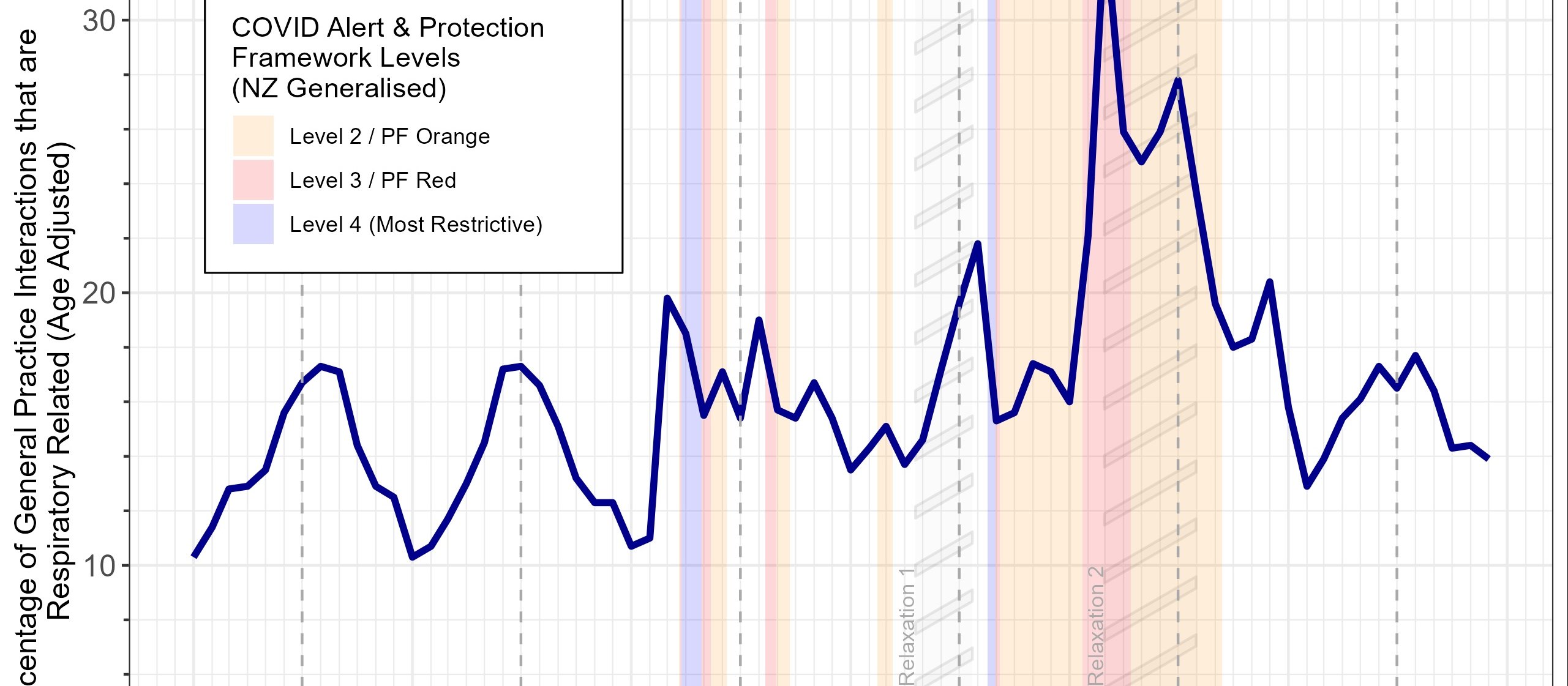
This article presents some major themes from research into the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on other viral respiratory illnesses
Kia ora and welcome to New Zealand Doctor Rata Aotearoa
Not a subscriber? Unlock this article by subscribing here.
1. Huang QS, Turner N, Wood T, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 related border restrictions on influenza and other common respiratory viral infections in New Zealand. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2024;18(2):e13247.
2. Turner N, Aminisani N, Huang S, et al. Comparison of the burden and temporal pattern of hospitalisations associated with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) before and after COVID-19 in New Zealand. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2024;18(7):e13346.
3. ESR. Respiratory Illness Dashboard.
4. Dowell A, Huang S, McIntosh C, et al. Towards new forms of communication and surveillance: a mixed methods study of rapid respiratory virus assessment in general practice during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. J Prim Health Care 2024;16 July online.



